Cover story previously published in Rite Up, 2021 – Issue 3.
by Hayley Hair
The Comeback is Bigger Than the Setback
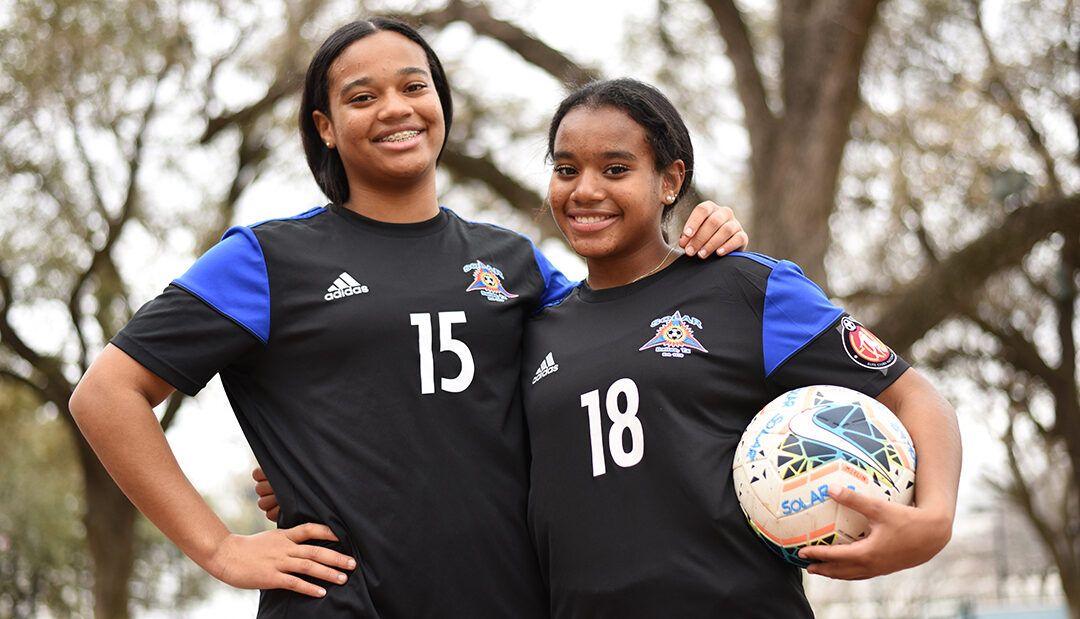
On the wide-open field under the scorching summer sun, soccer player Lillian lines up her kick and launches the soccer ball through the air hurtling toward the goal. Today she’s in practice leading up to her select soccer team’s upcoming season. Last fall’s season looked dramatically different as an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) rupture and meniscus tear took 12-year-old Lillian and her parents not only by surprise but also, unfortunately, out of the game.
“I was in the far corner and a girl hit me from the side,” Lillian says. “I heard several pops, and then I was on the ground in tears. It was just the most painful thing.” Lillian was able to limp away after the injury, but it hurt, and the pain persisted. Lillian’s mother, Debbie, set up a doctor’s appointment to have Lillian’s knee examined. “I had this vision that an ACL injury was excruciating, and you couldn’t walk,” Debbie says. “She was in pain, but not what I thought it would look like. It hurt, but she was mobile.”
Following X-rays and an MRI, Lillian’s injury was confirmed. “Just hearing the doctor say, ‘torn ACL,’ I couldn’t think of anything. My mind just stopped,” Lillian says. Later that day and feeling overwhelmed about her future sports goals, Lillian searched online to find out what professional athletes experienced injuries like hers. Then she saw her soccer idol’s name pop up on the list. “It’s happened to a lot of professional players, like Alex Morgan, who I’ve looked up to my entire life. That kind of comforted me.”
The Ins and Outs of ACL Injuries in Children
The ACL is a stabilizing ligament in the central part of the knee that stabilizes translation and rotation of the joint and is typically injured in pivoting, twisting and agility sports. Over the last several decades, recognition of ACL injuries has increased, and rupturing the ACL is particularly common in female soccer.
One hears about torn ACLs frequently in adult sports, but what happens when the injury presents in children? Lillian’s X-rays showed that her growth plates were still open, signaling plenty of growing in her future, so her best bet for care would be provided by a pediatric orthopedic specialist. She was referred to Scottish Rite for Children’s Orthopedics and Sports Medicine Center in Frisco and into the care of pediatric orthopedic surgeon Philip L. Wilson, M.D., assistant chief of staff and director of the Center for Excellence in Sports Medicine.
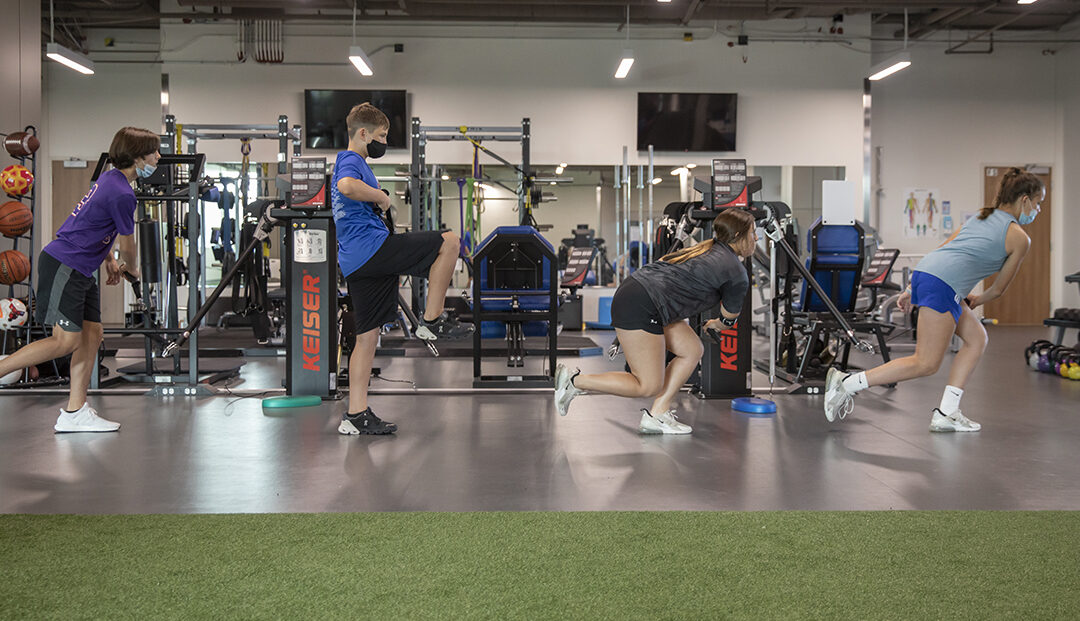
For a growing athlete, the experts at Scottish Rite for Children have unparalleled experience providing non-operative and arthroscopic care to treat common sport-related injuries including concussions, ligament injuries and cartilage conditions in the knee, ankle, shoulder, elbow and hip.
“Some ACL injuries may not need to be reconstructed if there are no cartilage injuries or shifting or instability of the knee,” Wilson says. “Unfortunately, this is less common, and despite rehabilitation, many children need surgery due to laxity in their ligaments and their high activity levels.” For Debbie and Sergio, Lillian’s parents, Wilson was the perfect fit for determining their daughter’s care.
“Dr. Wilson sat with me and my daughter and answered every question I had under the sun about the data, his experience and his research. He was an open book about everything,” Debbie says. “The whole team was positive. They made us feel like we had a great plan in place and that it’s all going to be just fine.”
The Right Surgical Technique for Patients Like Lillian
That research Wilson reviewed with the family is the novel ACL surgical technique for growing athletes that he and pediatric orthopedic surgeon Henry B. Ellis, M.D., created and subsequently published in the American Journal of Sports Medicine and presented at the annual meetings of the Pediatric Orthopedic Society of North America and the American Orthopedic Society of Sports Medicine.
“We have found in our research at Scottish Rite studying a particular technique that we developed that this can cut ACL reinjury rates in half,” Wilson says. “Female adolescent soccer players, like Lillian, have a particularly high risk of reinjury, sometimes as high as 25%, which is the highest that we have recorded in youth and young adult sports. Adding the stabilizing ligament helps reduce that reinjury risk. She also had cartilage repair, which is common is 70% in our ACL injury population.”
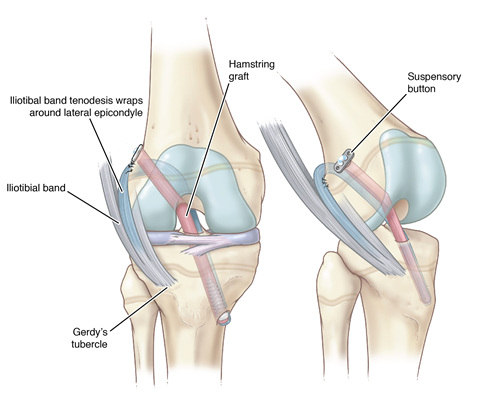
Lillian had a quadriceps tendon autograft for her ACL repair. She also had a lateral tenodesis with her iliotibial band, which means Wilson used a strip of tissue from the side of the knee to add a secondary stabilizing ligament that helps control rotation and protect the knee.
“There’s nothing you can tell a parent to put them at ease when their child is going through the actual procedure,” Sergio says. “There’s nothing routine when someone puts your child under anesthesia, but when you are in a facility like Scottish Rite, in a place where the doctors are proven performers, that gives you peace of mind.”