Mastering Daily Tasks To Help Others Feel Their Best
Previously published in Rite Up, 2024 – Issue 2.
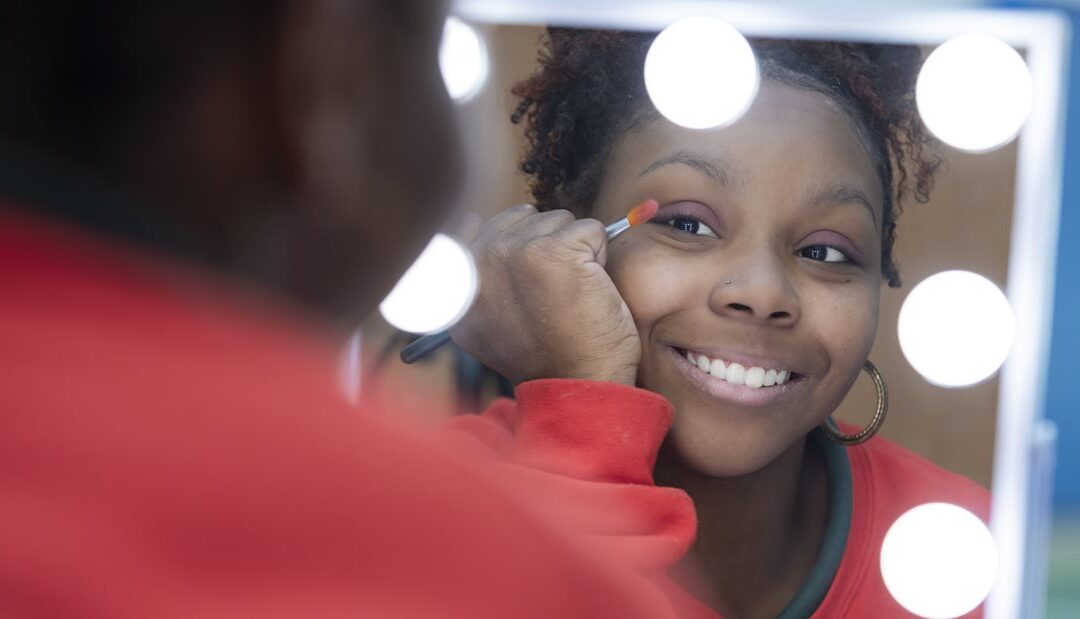
Fifteen-year-old Zion, of Glenn Heights, is preparing to become an esthetician when she graduates from high school. Her mother, Tiffany, bought her a mannequin that she uses to practice giving facials and applying makeup. “I want to make people feel good about themselves,” Zion says. “Being an esthetician will help people relax.” Recently, Zion brought her mannequin to Scottish Rite where she works with occupational therapist Lucy Ericson on mastering a host of daily activities.
Zion has cerebral palsy (CP) and has received care at Scottish Rite for Children since she was 10, after her family moved to Texas from Arizona. CP is the most common childhood disorder that affects muscles and movement. Zion’s symptoms impact her mobility, muscle coordination, flexibility and posture.
“It’s hard to walk around the mall, our neighborhood or around school because classes aren’t close together,” Zion says. She uses a wheelchair for long distances. “Sometimes, I force myself to walk, but I get very tired.” She also finds it challenging to do things with her right hand, like twisting open a jar, pouring juice or writing essays. “It’s hard keeping my hand straight,” she says, “but that’s why we go to Lucy.”
In occupational therapy, Zion works through a list of tasks that she conquers one by one. Lucy has helped her find creative ways to brush her teeth, wash her skin, cook food, open a pill bottle, roll her wheelchair by herself, get binders in and out of her backpack, put on earrings and apply makeup, like eye shadow and lip gloss. “It makes me feel really good,” Zion says. “I never thought I was going to be able to do all that stuff by myself.”
As tasks get easier for Zion to achieve, she prepares for her future as an esthetician. “Zion wants to be ready when she graduates so there aren’t any barriers,” Tiffany says. In a session with Lucy, Zion massages the mannequin’s face with shaving cream. “We’re not using the high-end stuff on a mannequin,” Tiffany says, laughing, but then, her tone turns bittersweet as she considers the years they have spent at Scottish Rite. “They make us feel like we are part of one big family,” she says. Zion underscores how much it means to her. “I really love, gosh, all the people,” she says. “I couldn’t imagine myself being able to do what I can do without Scottish Rite’s help.”






-LR.jpg?width=600&height=378)